Romania
Romanian Team Preparation Activities.
Research for the youth exchange KA152YOU: PLAN to PLANT GREEN PLAN TO PLANT (GREPLA-PLA)
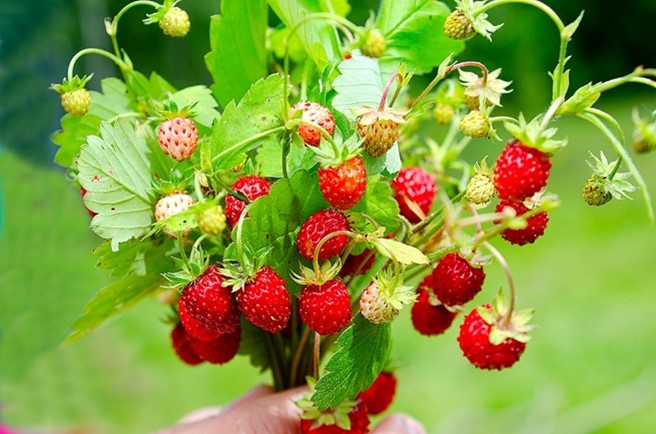
Alpine strawberry, Woodland strawberry
It is a temperate plant. It grows in the highlands in the tropics. It grows from 1600 m up to 3550 m in the tropics. They do poorly in hot humid climates. It needs well drained soils and a protected sunny position. They enjoy acid soil.
It can be found in Romania, Serbia, Bulgaria, but not in Portugal, Greece or Cyprus.

Cultivation: They can be grown from seed or wild in some areas.
Edible Uses: The fruit is eaten fresh with ice cream or as a filling for tarts or made into jam. The dried leaves are used to make tea. It has a good flavour and is high in Vit C. Young leaves are eaten in salads and soups.

Couch
It grows in warm temperate and tropical places. It is a weed of crops in many countries and It grows better on fertile soils, in wetlands, but It can grow also in arid places.
It can be found in Romania, Cyprus, Greece, Portugal, Bulgaria, but not in Serbia.
Cultivation: Plants grow from sections of the creeping stems.
Edible Uses: The tender leaves are edible cooked. They are also crushed and the juice used to make a drink. The rhizomes or underground stems are eaten raw as a snack and also ground into flour to make bread. They are dried and used as a spice. The leaves and stems are cooked in curries. Plants can have cyanide so should be cooked.

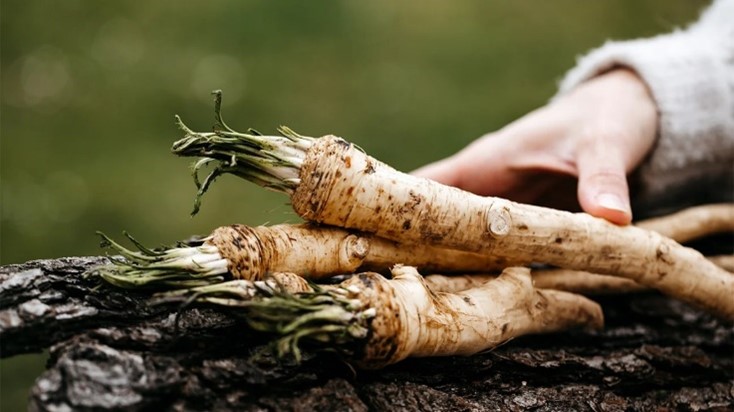
Horseradish
It suits temperate places. Plants grow readily in most soils and in moist semi-shaded conditions. In the tropics it is cultivated in mountainous places.
It can be found in Romania, Bulgaria, Serbia, but not in Greece, Portugal or Cyprus.
Cultivation: They are grown by dividing roots. Roots are lifted as cold temperatures approach as the cold improves the flavour.
Edible Uses: The root is processed to produce horseradish sauce. It is ground finely and added to whipped cream. It is not cooked but used cold like mustard with cold meats. The fresh roots are used to flavour meats, vegetables and pickles. The young leaves can be added to salads and used in soups and sauce. They are a spice. CAUTION: Horseradish is a flavouring and should only be eaten in small quantities.

Russian olive
It is native to western Asia and It grows along coasts and near riverbanks and in dry riverbeds and floodplains. It does best with warm dry summers, It can tolerate salt soil. It needs plenty of sunlight and It is frost hardy. It can grow in arid places.
It can be found in Romania, Portugal, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Greece, but not in Serbia.
Cultivation: Plants can be grown from seed, cuttings, grafting or rooted suckers.
Edible Uses: The fruit is eaten dried and raw or cooked. The ripe fruit is sweet. They are also used for fermenting and distilling an alcoholic drink.

Yellow wood-sorrel
It can grow from tropical to warm temperate places. It grows in wetlands or in arid places.
It can be found in Romania, Greece, Bulgaria, Portugal, but not in Cyprus or Serbia.
Cultivation: Plants are grown from seed. They can also be grown from rooted cuttings of the branches.
Edible Uses: The young leaves are chewed when fresh. They are also pickled or used in chutney. The leaves are sour and can be added to salads. They can be cooked as a potherb. It is best to blanch them in boiled water then soaking in cold water for 2 hours. The leaves can be soaked in hot water for 10 minutes to make a drink. The ripe fruit are eaten fresh. CAUTION: Because the plant contains oxalates, eating it over extended periods can reduce the bodies ability to absorb calcium. It is best to eat it with some source of readily available calcium such as coconut milk or cream.

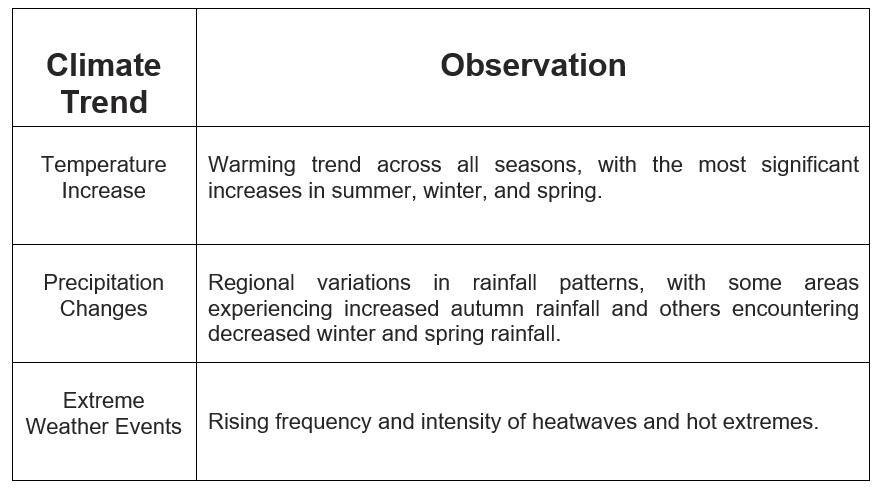
Effects of global warming in Romania
Economic
effects
Environmental changes have a significant impact on Romania's economy, touching various sectors and influencing both short-term and long-term economic stability and growth. Here are some of the key effects:
Agriculture:
- Climate Variability: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect crop yields. For instance, increased frequency of droughts and floods can lead to crop failures, affecting food supply and agricultural exports.
- Soil Degradation: Intensive farming practices combined with climate change can lead to soil erosion and loss of fertility, reducing agricultural productivity.

Energy Sector:
- Hydropower: Romania relies heavily on hydropower for electricity. Changes in precipitation patterns and river flows due to climate change can impact the reliability and capacity of hydropower plants.
- Renewable Energy: The country has potential for wind and solar energy. Climate changes can influence the effectiveness of these energy sources, either positively or negatively, depending on the region and the specific climatic shifts.
Forestry:
- Forest Health: Increased temperatures and changes in precipitation can lead to more frequent forest fires, pest infestations, and diseases, threatening the health and productivity of forests.
- Economic Impact: The forestry sector is important for Romania's economy. Damage to forests can lead to economic losses in timber production and related industries.
- Water Resources:
Water Availability:
- Climate change affects the availability of water resources. Changes in precipitation and increased evaporation rates can lead to water shortages, impacting agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
- Flooding: Increased frequency and intensity of floods can cause significant economic damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
